
Introduction to Corneal Treatment
Diabetic retinopathy is a severe eye condition that affects individuals with diabetes. As a leading vitreo-retina surgeon in Ramgarh, Jharkhand, Dr. Archana Kumari has extensive experience in diagnosing and treating diabetic retinopathy. This comprehensive guide aims to provide detailed information on diabetic retinopathy treatment, following best practices for SEO to ensure it meets all quality standards.
Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy
What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy is an eye complication caused by diabetes. It is caused by damage to the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. If left untreated, it can lead to blindness. According to the American Diabetes Association, nearly 40% of diabetic patients over the age of 40 have some degree of diabetic retinopathy, making it one of the leading causes of vision impairment and blindness globally.
Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy
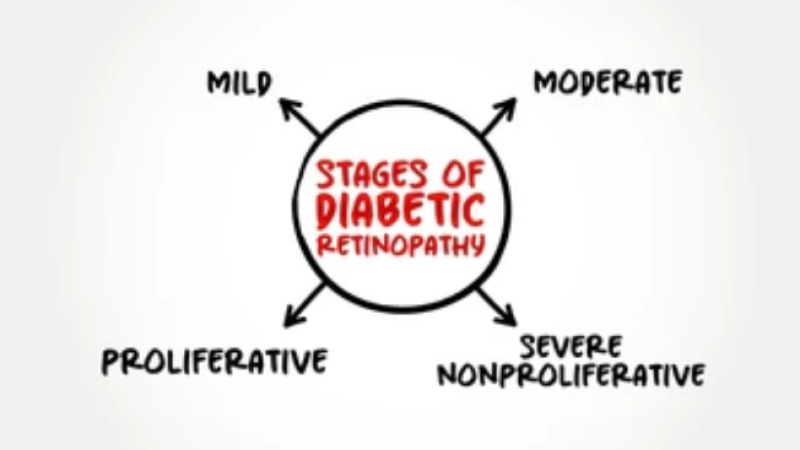
- Mild Nonproliferative Retinopathy: This early stage is characterized by small balloon-like swelling in the retina’s blood vessels. These microaneurysms may leak fluid into the retina, causing swelling.
- Moderate Nonproliferative Retinopathy: At this stage, some of the blood vessels that nourish the retina are blocked. This can lead to further changes in the retina’s appearance and function.
- Severe Nonproliferative Retinopathy: More blood vessels become obstructed, leading to multiple areas of the retina being deprived of their blood supply. These areas send signals to the body to grow new blood vessels.
- Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy: This is the advanced stage where the signals sent by the retina for nourishment trigger the growth of new blood vessels. These new blood vessels are abnormal and fragile, which can lead to severe vision problems, including bleeding into the vitreous, retinal detachment, and glaucoma.
Causes and Risk Factors
Causes
Diabetic retinopathy is primarily caused by prolonged high blood sugar levels that damage the blood vessels in the retina. Other contributing factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and smoking. The damage to retinal blood vessels leads to leakage, swelling, and reduced blood flow to the retina, causing vision impairment.
Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to an increased risk of developing diabetic retinopathy:
- Duration of diabetes: The longer you have diabetes, the higher the risk.
- Poor control of blood sugar levels: Consistently high blood sugar levels increase the likelihood of developing retinopathy.
- High blood pressure: Hypertension can exacerbate the damage to retinal blood vessels.
- High cholesterol levels: Elevated cholesterol levels can lead to the formation of fatty deposits in the blood vessels, worsening the condition.
- Pregnancy: Pregnancy can worsen diabetic retinopathy.
- Tobacco use: Smoking can increase the risk of diabetic complications, including retinopathy.
Symptoms
Early Symptoms
Diabetic retinopathy often has no early warning signs. Symptoms may include:
- Blurred vision
- Floaters (dark spots or strings)
- Difficulty seeing at night
- Colors appearing faded
Advanced Symptoms
As the condition progresses, symptoms can worsen, leading to:
- Severe vision loss
- Dark or empty areas in vision
- Difficulty reading or recognizing faces
- Sudden vision changes or loss
It’s crucial to monitor these symptoms and seek prompt medical attention if any changes in vision occur.
Diagnosis
Comprehensive Eye Exam
A comprehensive eye exam is crucial for diagnosing diabetic retinopathy. It includes:
- Visual acuity test: This test measures the ability to see at various distances.
- Dilated eye exam: Drops are placed in your eyes to dilate (widen) the pupils, allowing the doctor to examine the retina and optic nerve for signs of damage.
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT): This imaging test provides detailed cross-sectional images of the retina, allowing the doctor to detect swelling, fluid, or other changes in retinal thickness.
- Fluorescein angiography: This test involves injecting a special dye into your bloodstream. The dye travels to the blood vessels in your eyes, making them visible under a special camera. This helps to identify areas of blood vessel leakage or abnormal blood vessel growth.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection through regular eye exams is vital in managing diabetic retinopathy effectively and preventing severe vision loss. The American Academy of Ophthalmology recommends that people with diabetes have a comprehensive eye exam at least once a year. Early treatment can slow or even stop the progression of diabetic retinopathy and reduce the risk of vision loss.
Treatment Options
Laser Surgery
Laser surgery, or photocoagulation, is used to treat advanced stages of diabetic retinopathy by shrinking abnormal blood vessels. This procedure helps to prevent further leakage and reduce the risk of severe vision loss. Laser treatment can be categorized into:
- Focal Laser Treatment: Used to treat specific areas of leakage in the retina.
- Panretinal Photocoagulation: Involves treating the peripheral retina to reduce the growth of abnormal blood vessels.
Vitrectomy
Vitrectomy is a surgical procedure where the vitreous gel is removed and replaced to clear blood and scar tissue from the retina. This surgery is often recommended for patients with severe bleeding (vitreous hemorrhage) or retinal detachment. The goal of vitrectomy is to restore normal retinal anatomy and improve vision.
Anti-VEGF Injections
Anti-VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) injections help reduce swelling and slow the growth of abnormal blood vessels. Medications such as ranibizumab (Lucentis), aflibercept (Eylea), and bevacizumab (Avastin) are commonly used. These injections can significantly improve vision and reduce the need for laser surgery.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids can be injected or implanted in the eye to reduce inflammation and swelling. They are often used in combination with other treatments, such as anti-VEGF injections. Corticosteroid implants, such as the dexamethasone implant (Ozurdex), provide sustained release of medication over several months.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Blood Sugar Control
Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and medication is crucial in managing diabetic retinopathy. Consistent blood sugar control can prevent or delay the onset of diabetic retinopathy. The American Diabetes Association recommends a target HbA1c level of less than 7% for most adults with diabetes.
Blood Pressure and Cholesterol Management
Regular monitoring and managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels are essential. High blood pressure and cholesterol can exacerbate the damage to retinal blood vessels, so keeping these levels in check can help protect your vision.
Regular Eye Exams
Regular eye exams, even if you don’t notice symptoms, can help detect early signs of diabetic retinopathy. Early detection allows for timely treatment and better management of the condition. Patients with diabetes should have a comprehensive eye exam at least once a year.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- Quit smoking: Smoking increases the risk of diabetic complications, including retinopathy.
- Maintain a healthy diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help control blood sugar levels.
- Exercise regularly: Physical activity helps improve blood sugar control and overall health.
- Monitor your vision: Keep track of any changes in your vision and report them to your doctor promptly.
Expert Insights from Dr. Archana Kumari
Prasad Eye Hospital in Ramgarh, Jharkhand, led by expert vitreo-retina surgeon Dr. Archana Kumari, is the best choice for diabetic retinopathy treatment. The hospital offers state-of-the-art diagnostics and advanced treatments like laser surgery and anti-VEGF injections. With a multidisciplinary team and a commitment to patient education and support, Prasad Eye Hospital ensures comprehensive and personalized care. “Early detection and timely treatment are key in managing diabetic retinopathy. Patients should not overlook regular eye check-ups, even if they feel their vision is fine. Managing blood sugar levels and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are crucial steps in preventing the progression of this condition.”
Book an Appointment
Early detection and timely treatment are crucial for diabetic retinopathy. Schedule an appointment with Dr. Archana Kumari at Prasad Eye Hospital in Ramgarh, Jharkhand, for expert diabetic retinopathy treatment. Contact us today to preserve your vision and maintain your eye health.
